DBJ's Environmental Management
DBJ not only strives to reduce the environmental impact of its operations but also actively pursues environmental activities with full member participation in the projects it supports.
Alignment with UNEP FI
In June 2001, DBJ became the first Japanese bank to sign the UNEP Statement by Financial Institutions on the Environment and Sustainable Development, promising to strive for harmony between economic development and environmental conservation and to cooperate in resolving environmental problems. Since joining the UNEP FI, the Bank has continued to work with the UNEP FI and other institutions to pursue measures in accordance with the UNEP Statement's intent.
As part of these efforts, the UNEP FI 2003 Global Roundtable in Tokyo was held in October 2003. DBJ co-sponsored the meeting, under the theme “Sustaining Value: Finance's Roles in Creating a Sustainable Society and Realizing Value,” as a representative of the Japanese financial institutions that have joined the UNEP FI. The Tokyo Principles were issued in the form of a conference statement for this meeting.
DBJ's Environmental Management
DBJ recognizes the resolution of environmental problems as an issue that is common to all humankind. Based on its Policy on Sustainability, DBJ aims to contribute to the sustainable development of Japan and the world by its environmental activities as follows
Promoting Environmental Measures through Loan and Investment Activities
- Through its investment and loan activities, DBJ supports global warming prevention measures and the promotion of a recycling-oriented society. In addition, by supporting environmentally sustainable corporate management by its clients, DBJ contributes to their creation of environmental measures and to the realization of a sustainable society.
- DBJ contributes to clients' environmental measures through the risk evaluations of investment and loan activities from an environmental perspective.
Promotion of environmental awareness through environmental communication
- Through continuing research and advisory activities relating to environmental issues, DBJ seeks to help resolve environmental issues through enhanced awareness, thereby contributing to the realization of a sustainable society.
- DBJ seeks to promote environmental awareness through international cooperation, including the distribution of information about environmental initiatives by Japan.
- DBJ endeavors to improve its initiatives by sharing information on its environmental activities and through communication with society.
Promotion of environmental awareness activities in offices
- DBJ complies with environmental laws and regulations, promotes activities to reduce the environmental impact of its operations. To these ends, DBJ seeks to contribute to the creation of environmentally friendly office environments through the activities indicated below.
- (1)
Promotion of resource and energy conservation and recycling activities
- (2)
Promotion of environmentally friendly sourcing of supplies
- (3)
Prevention of environmental pollution
- (1)
Promotion of environmental awareness activities in communities
- By cooperating with community environmental improvement initiatives, such as measures to prevent heat islands, DBJ works to contribute to the creation of environmentally friendly regional societies.
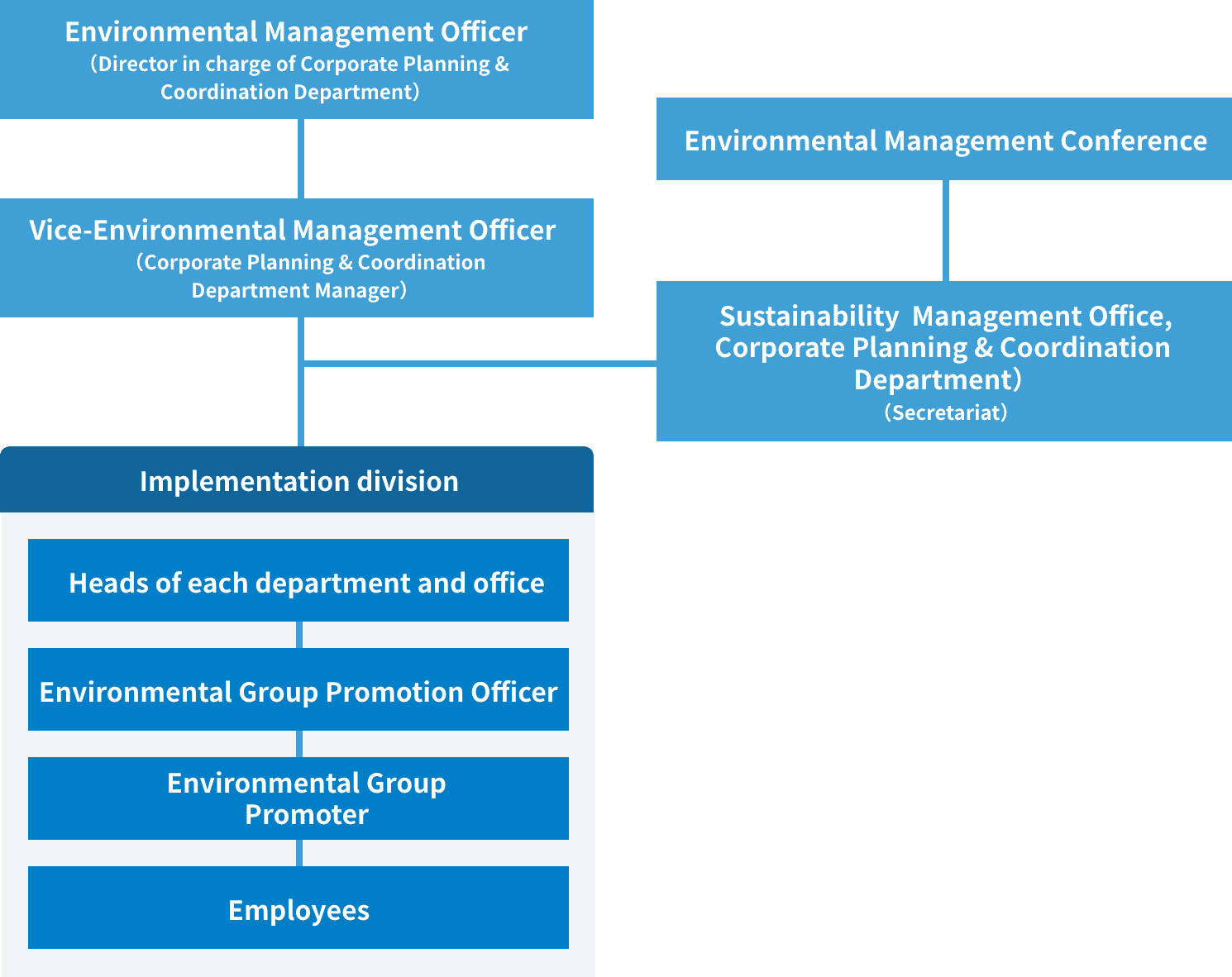
DBJ's Environmental Management Structure
Efforts to Conserve Resources and Energy
As part of its environmental management system, DBJ sets numerical targets and uses posters and other means to enlighten employees.
Green Purchasing
DBJ has set annual numerical goals for purchasing products and services effective in reducing environmental impacts.
Global Warming Research Center
DBJ has established the Global Warming Research Center within its Research Institute of Capital Formation. The center tackles global warming and other worldwide environmental issues by conducting academic research, centering on economic research.
Hirofumi Uzawa, an economist and professor emeritus of Tokyo University, acts as special advisor to a research group at the center that conducts basic research on links between economic activity and the environment, from three principal perspectives.
- 1.
Conduct theoretical economic research and empirical analysis concerning atmospheric stabilization and the global environment
- 2.
Analyze the natural environment as shared social capital
- 3.
Analyze infrastructure and structure capital
Through analysis conducted by the Global Warming Research Center, DBJ provides theoretical support to activities in the environmental arena. In addition, the Bank publishes books and discussion papers and conducts symposia. Through these efforts and the center's research results, the Bank seeks to contribute to society in a broad sense.
Major Activities to Date
Research on cities as shared social capital
The center conducted a comparative study of Japanese and European cities from the perspective of natural environments and system capital, offering suggestions of ideal urban environments in the 21st century
Construction of a dynamic general equilibrium model (in process)
Studying the impact on long-term growth patterns of the Japan economy of using carbon taxes as a policy to stabilize carbon dioxide emissions
Participation in an international symposium at the International University of the United Nations (October 1999)
Participated in “The Global Environment and Economic Theory,” an International Symposium for International Research hosted by the International University of the United Nations, debating on the global economy and sustainable development
Hosted an international symposium (November 1995)
The center hosted the international symposium “Considering Global Environmental Issues: What is Expected of Japan?” Participants included well-known economic researchers from Japan and overseas (nine researchers, including Hirofumi Uzawa, K.J. Arrow and D.W. Jorgensen), who debated on global warming and economic growth
- Sustainability
- Sustainability News
- Message from the President
- Sustainability Management System
- Policy on Sustainability
- DBJ Group Human Rights Policy
- Value Creation Process
- Priority Areas for the Achievement of Vision 2030
- Resolving Social Issues and Creating Value Through Our Core Businesses
- Fundamental Activities
- Collaboration with Stakeholders






























