Corporate Governance
Basic Position on Corporate Governance
DBJ is governed by the Development Bank of Japan Inc. Act (the DBJ Act) in accordance with the following objective.
Article 1
Development Bank of Japan Inc. (hereinafter referred to as the “Corporation”) shall be a joint-stock company (kabushiki-kaisha) whose objective is to contribute to the smooth supply of funds to those needing long-term business funds, as well as to the sophistication of financial functions.
DBJ is working to enhance its unique governance system in addition to usual management supervision as a company with a board of directors and company auditors (Audit & Supervisory Board), through a business model built upon features such as integrated investments and loans and proper execution of the preceding objective, in order to raise the value of tangible and intangible management resources to be invested and to realize sustainable management that aims for both economic and social value.
Specifically, the 2015 revisions to the DBJ Act established Special Investment Operations and obligatory measures to be considered, requiring that DBJ conduct its operations in a manner that does not obstruct appropriate competitive relations with other entities, in particular, applying these requirements to the Advisory Board, made up of outside experts and outside members of the Board of Directors, and the Special Investment Operations Monitoring Board, composed of outside experts, which function as advisory bodies to the Board of Directors. These bodies provide advice on DBJ’s overall management and deliberate and evaluate business results, including consistency with the policy objectives of Special Investment Operations, ensuring that appropriate competitive relations are maintained with private financial institutions.
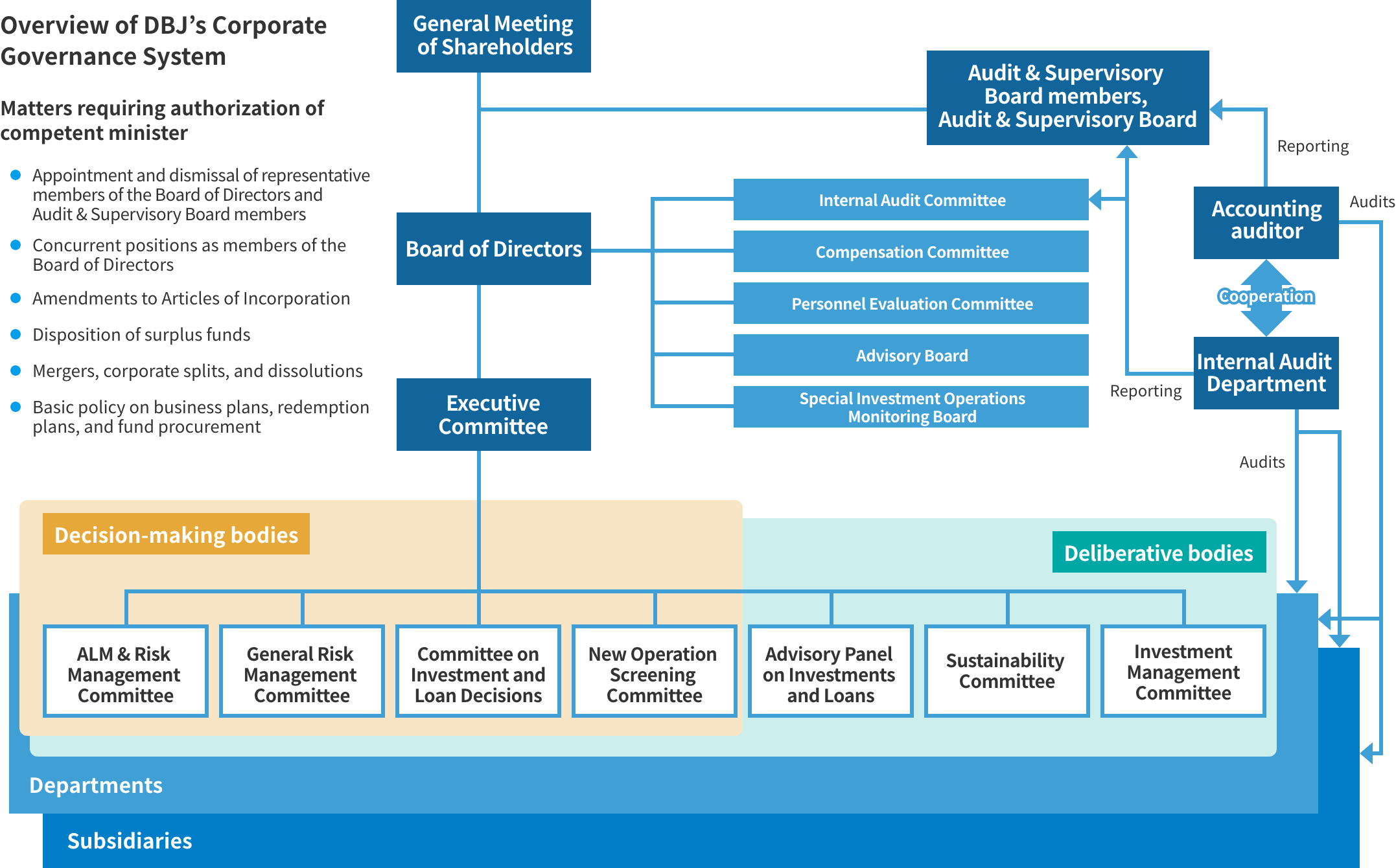
DBJ’s Corporate Governance System
| Institutional design configuration | A company with a board of directors and company auditors (Audit & Supervisory Board) |
|---|---|
| Number of members of the Board of Directors | 10 |
| Of whom are outside members | (2) |
| Number of Board of Directors’ meetings in fiscal 2021 | 14 |
| Number of Audit & Supervisory Board members | 5 |
| Of whom are outside members | (3) |
| Number of Audit & Supervisory Board meetings in fiscal 2021 | 14 |
| Adoption of executive officer system | Yes |
| Accounting auditor | Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu LLC |
Audit & Supervisory Board Members, Audit & Supervisory Board
The Audit & Supervisory Board comprises five members. The Companies Act prescribes that a majority of Audit & Supervisory Board members be outside members (in DBJ’s case, three of the five). DBJ offices contribute three members (two members proper to DBJ and one an outside member).
Also, DBJ has created the Audit & Supervisory Board Office, which, under the board’s direction, assists board members, including outside members, in performing their duties. The Audit & Supervisory Board and Audit & Supervisory Board members audit the execution of duties by members of the Board of Directors, based on their audit policy and audit plans.
Audit & Supervisory Board members attend Board of Directors’ and other important meetings and may query the execution of business by members of the Board of Directors, peruse documents, and conduct audits at branches and subsidiaries.
Advisory Bodies to the Board of Directors
In pursuit of sustainability management and corporate objectives, the following advisory bodies to the Board of Directors have been established for the purpose of maintaining transparency in management and to reflect the knowledge of outside experts.
Internal Audit Committee
The Board of Directors has established the Internal Audit Committee, delegating to this body the authority to deliberate important matters related to internal audits. This committee met three times during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Compensation Committee
The Compensation Committee, the majority of which consists of outside executives, considers the type of executive compensation structure that befits DBJ from the standpoint of ensuring transparency and objectivity regarding compensation.
Personnel Evaluation Committee
The Personnel Evaluation Committee, composed of outside members of the Board of Directors and other outside experts, evaluates personnel proposals on the selection of members of the Board of Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board members.
Advisory Board
Since DBJ’s establishment as a joint-stock company in October 2008, the Advisory Board has been in place as an advisory body to the Executive Committee, providing advice on overall management. Revisions in 2015 to the DBJ Act stipulate for an indefinite period obligatory measures to be considered—in particular, requiring that DBJ conduct its operations in a manner that would not obstruct appropriate competitive relations with other entities. Accordingly, this board is positioned anew as an advisory body to the Board of Directors. As one of its roles, even more than before, the Advisory Board is tasked with deliberating and evaluating important matters related to ensuring that appropriate competitive relations are maintained with private financial institutions.
This board convened twice during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022. It is composed of the following outside members of the Board of Directors and outside experts in fields including manufacturing, infrastructure, regional communities, and finance.
Special Investment Operations Monitoring Board
One of the measures of the 2015 revisions to the DBJ Act was in regard to Special Investment Operations. The act stipulates the establishment of a Special Investment Operations Monitoring Board as an advisory body to the Board of Directors. This monitoring board is tasked with deliberating projects and evaluating their performance in terms of appropriateness against policy objectives and with emboldening private-sector enterprises and complementing their operations while maintaining appropriate competitive relations. This board, whose members include outside experts from private-sector financial institutions and capital markets, convened twice during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Moreover, in order to examine whether appropriate competitive relations with other entities are being maintained, roundtable discussions are held regularly with the Japanese Bankers Association, the Regional Banks Association of Japan, and the Second Association of Regional Banks, including these entities’ private financial institution members. Each group met twice in fiscal 2021, for a total of six meetings. Disputes and opinions raised in these meetings are reported to and deliberated by the Advisory Board and the Special Investment Operations Monitoring Board.
Executive Committee
The Board of Directors has vested in the Executive Committee decision-making authority regarding the execution of business.
Accordingly, the Executive Committee makes important management decisions. The committee met 31 times during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Committees under the Executive Committee
| Name | Role |
|---|---|
| ALM & Risk Management Committee | This committee deliberates and makes decisions pertaining to portfolio risk management and asset–liability management. |
| General Risk Management Committee | This committee deliberates and makes decisions on important items related to operational risk management, system risk management, legal compliance, responses to antisocial forces, client protection management, and other important items. |
| Committee on Investment and Loan Decisions | This committee handles, deliberates, and makes decisions related to investments and loans, overseas business strategy, and operations and management conditions. |
| New Operation Screening Committee | This committee deliberates and makes decisions on the commencement of initiatives involving new businesses. |
| Advisory Panel on Investments and Loans | This panel handles the advance deliberation on and monitoring of investments and loans as well as deliberations on overseas business strategy and operations and management conditions. |
| Sustainability Committee | This committee deliberates on items related to both economic and social value as well as dialogue with stakeholders. |
| Investment Management Committee | This committee monitors investment projects and enhances the monitoring system, as well as discussing planned proposals for investment policies. |
Internal Audits
DBJ has established the Internal Audit Department under the direct supervision of the president and CEO of DBJ and independent of other operating departments. The department conducts inspections to ensure the appropriateness and effectiveness of internal controls, including overall operational compliance and risk management, and performs evaluations and recommends improvements. The Internal Audit Committee deliberates and decides audit plans, audit reports, and other important matters related to internal audits, and this information is reported to the Board of Directors. As of June 29, 2022, 25 people belonged to the Internal Audit Department.
Accounting Audits
DBJ has in place an agreement whereby Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu LLC conducts accounting audits as the Company’s accounting auditor in accordance with Article 396, Paragraph 1 of the Companies Act and Article 193, Paragraph 2 (i) of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act.
Three-Pronged Auditing Approach
DBJ’s Audit & Supervisory Board members, the Internal Audit Department, and the accounting auditor periodically and as necessary exchange opinions and information, and communicate in an effort to ensure effective and appropriate audits.
Executive Compensation
DBJ’s Compensation Committee is an advisory body to the Board of Directors. It deliberates on the compensation structure for members of the Board of Directors and evaluates the propriety of the compensation structure for the Company. The majority of its members are outside executives.
DBJ takes the following basic approach to executive compensation.
- Compensation should reflect social trends in regard to executive pay.
- Compensation should provide motivation for initiatives aimed at realizing economic and social value during each fiscal year and in the medium to long term
In accordance with this approach, DBJ provides compensation to its executives in three forms: fixed compensation, executive bonuses, and executive retirement benefits.
- (1)
Fixed compensation is paid monthly in an amount based on the executive’s position.
- (2)
Executive bonuses are distributed after taking into consideration the performance of each member of the Board of Directors in carrying out their duties during the fiscal year. Bonuses start with a standard amount based on the position of the member of the Board of Directors. Bonuses also include a quantitative assessment portion determined based on a preset distribution percentage that reflects the achievement of the consolidated net income target, as well as a qualitative assessment portion determined based on a preset distribution percentage that comprehensively considers each executive’s achievement of performance targets in their business division. Consolidated net income (¥46,815 million in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2021) is used as the performance indicator because it most accurately reflects DBJ’s performance.
- (3)
Executive retirement benefits are paid out upon retirement in an amount reflecting successful service over the longer term.
Below is a description of the compensation structure for members of the Board of Directors.
Compensation for full-time members of the Board of Directors consists of fixed compensation, executive bonuses,and executive retirement benefits. To maintain their independence, part-time members of the Board of Directors receive fixed compensation alone.
Compensation for full-time Audit & Supervisory Board members comprises fixed compensation, and executive retirement benefits. Compensation for part-time Audit & SupervisoryBoard members consists solely of fixed compensation.
The amount of compensation paid to members of the Board of Directors is determined after deliberation by the Board of Directors, within the maximum amount approved at the General Meeting of Shareholders following discussions by the Compensation Committee. Compensation amounts are based on the position and responsibilities of each member of the Board of Directors, with due consideration given to social trends, DBJ’s financial performance, and other standards balanced against employee salaries. The Articles of Incorporation limit the number of directors to 13 or less.
The General Meeting of Shareholders held on June 29,2017, passed a resolution that sets ¥270 million as the maximum annual amount for total compensation paid to members of the Board of Directors. The Company’s first General Meeting of Shareholders held on September 22, 2008, passed a resolution that sets ¥80 million as the maximum annual amount for total compensation paid to Audit & Supervisory Board members. The Articles of Incorporation set the number of Audit & Supervisory Board members to five or fewer.
The Compensation Committee was established in 2008 to ensure transparency and objectivity in the process for determining compensation, and a majority of members of the Compensation Committee comprises outside executives. This composition allows independent outside executives to be involved and give relevant advice.
Please refer to the links below for detailed information regarding DBJ’s corporate governance.
Compliance
This section describes DBJ's basic approach, initiatives and policies in regard to compliance.
Compliance- Sustainability
- Sustainability News
- Message from the President
- Sustainability Management System
- Policy on Sustainability
- DBJ Group Human Rights Policy
- Value Creation Process
- Priority Areas for the Achievement of Vision 2030
- Resolving Social Issues and Creating Value Through Our Core Businesses
- Fundamental Activities
- Collaboration with Stakeholders






























